工具一:Json Server
简介
json-server是一款小巧的Mock工具,它可以不写一行代码在30秒内创建一套Restful风格的 api。相比较Django,flask来实现Mock要方便很多。
通俗来说,就是模拟服务端接口数据,一般用在前后端分离后,前端人员可以不依赖API开发,而在本地搭建一个JSON服务,自己产生测试数据。
主页地址:https://www.npmjs.com/package/json-server
Github项目地址:https://github.com/typicode/json-server
环境搭建
首选需要安装Node.js ,
国内用户建议配置好:cnpm
安装
cnpm install -g json-server
校验
安装完成后输入如下命令进行校验:
json-server -h
安装正确会提示如下内容:
C:\Users\12446>json-server -h
bin.js [options] <source>
Options:
-c, --config Path to config file
[default: "json-server.json"]
-p, --port Set port [default: 3000]
-H, --host Set host [default: "localhost"]
-w, --watch Watch file(s) [boolean]
-r, --routes Path to routes file
-m, --middlewares Paths to middleware files [array]
-s, --static Set static files directory
--read-only, --ro Allow only GET requests [boolean]
--no-cors, --nc Disable Cross-Origin Resource Sharing [boolean]
--no-gzip, --ng Disable GZIP Content-Encoding [boolean]
-S, --snapshots Set snapshots directory [default: "."]
-d, --delay Add delay to responses (ms)
-i, --id Set database id property (e.g. _id)
[default: "id"]
--foreignKeySuffix, --fks Set foreign key suffix (e.g. _id as in post_id)
[default: "Id"]
-q, --quiet Suppress log messages from output [boolean]
-h, --help Show help [boolean]
-v, --version Show version number [boolean]
Examples:
bin.js db.json
bin.js file.js
bin.js http://example.com/db.json
https://github.com/typicode/json-server
C:\Users\12446>
入门使用
创建json数据——db.json
在任意一个文件夹下(此处我创建了一个json_action文件夹),进入到该文件夹里面,执行代码:
json-server --watch db.json
执行成功后会多出一个db.json文件。
D:\项目\json_action>json-server --watch db.json
\{^_^}/ hi!
Loading db.json
Oops, db.json doesn't seem to exist
Creating db.json with some default data
Done
Resources
http://localhost:3000/posts
http://localhost:3000/comments
http://localhost:3000/profile
Home
http://localhost:3000
Type s + enter at any time to create a snapshot of the database
Watching...
此时我们可以访问 http://localhost:3000 (启动json-server后,点击才有效),看到如下页面: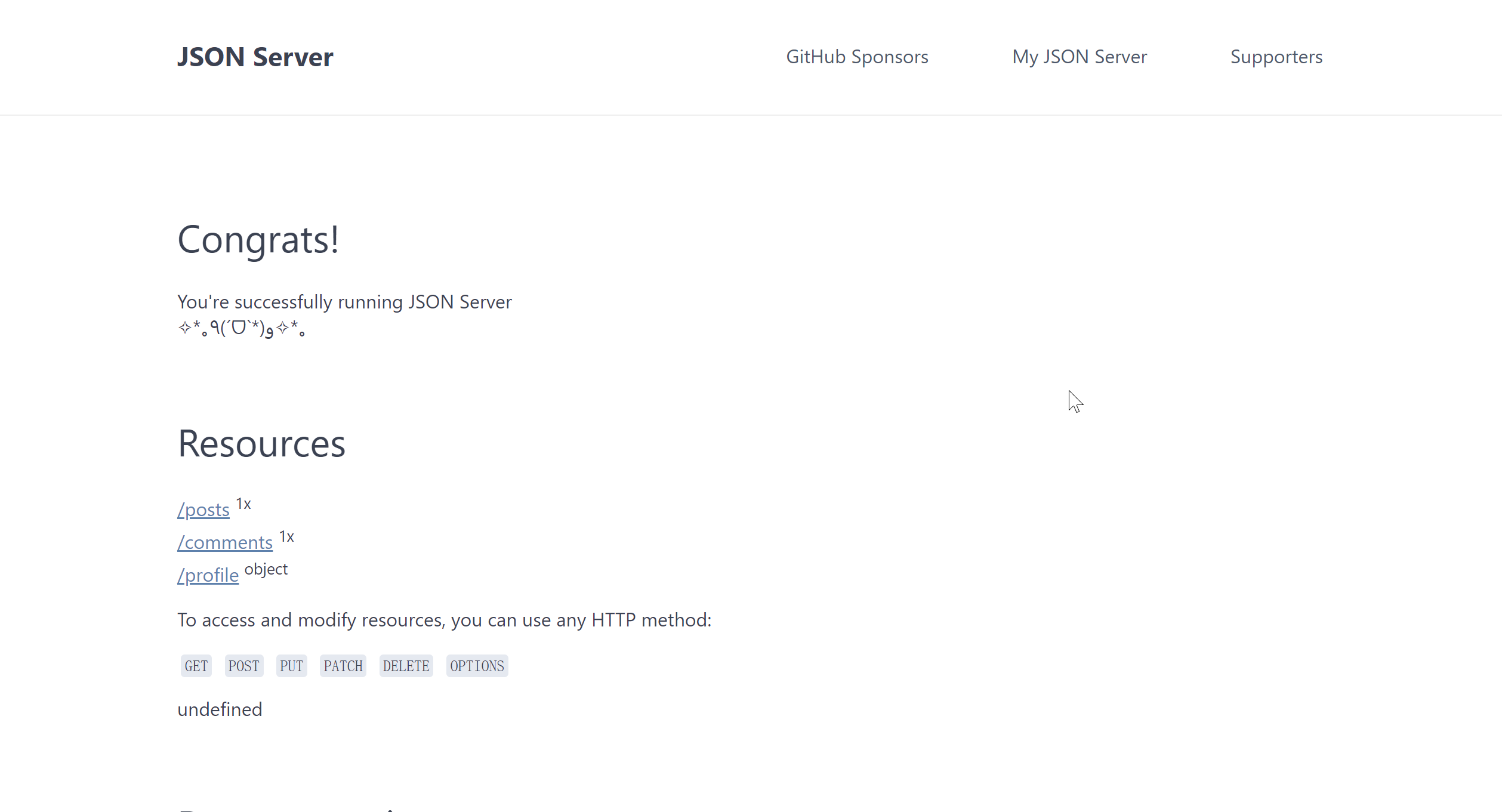
db.json里面自带的数据:
{
"posts": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "json-server",
"author": "typicode"
}
],
"comments": [
{
"id": 1,
"body": "some comment",
"postId": 1
}
],
"profile": {
"name": "typicode"
}
}
posts /comment /profile 分别是db.json里面的子对象。
修改端口号
json-server 默认是 3000 端口,我们也可以自己指定端口,指令如下:
json-server --watch db.json --port 3004
之后启动服务,只需要执行如下指令就可以了:
npm run mock
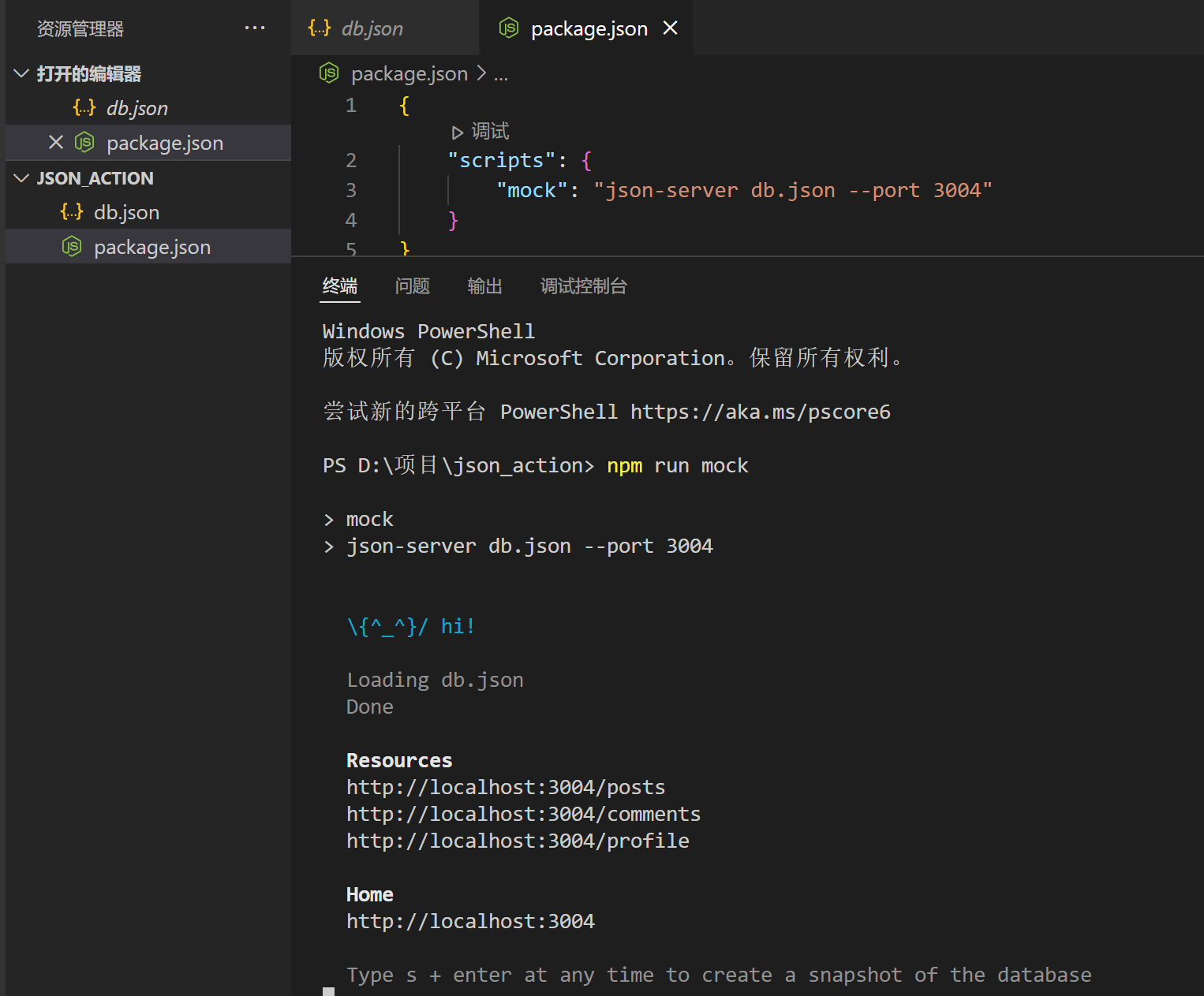
接口测试
操作数据
使用下面的db.json 数据
{
"posts": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "json-server",
"author": "typicode"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "json-server2",
"author": "typicode2"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "json-server3",
"author": {"name":"jack"}
}
],
"comments": [
{
"id": 1,
"body": "some comment",
"postId": 1
}
],
"profile": {
"name": "typicode"
}
}
接下来我们就可以GET, POST, PUT, PATCH or DELETE 方法来对数据进行操作。
获取数据
get直接获取
输入http://localhost:3004/posts 可以查看到对应的返回值:
浏览器地址访问就可以看做GET操作,所以不用写任何代码
[
{
"id": 1,
"title": "json-server",
"author": "typicode"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "json-server2",
"author": "typicode2"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "json-server3",
"author": {
"name": "jack"
}
}
]
可以得到所有posts 数据(对象数组)
过滤获取 Filter
根据id获取数据http://localhost:3004/posts/2
{
"id": 2,
"title": "json-server2",
"author": "typicode2"
}
可以指定id为1的获取指令还可以用如下指令,注意,此时返回的数据是一个数组。 http://localhost:3004/posts?id=2
[
{
"id": 2,
"title": "json-server2",
"author": "typicode2"
}
]
指定多个条件,用&符号连接:http://localhost:3004/posts?title=json-server2&author=typicode2
[
{
"id": 2,
"title": "json-server2",
"author": "typicode2"
}
]
指定过滤字段,使用.号可以查询更深层次属性http://localhost:3004/posts?author.name=jack
[
{
"id": 3,
"title": "json-server3",
"author": {
"name": "jack"
}
}
]
分页操作
分页采用 _page 来设置页码, _limit 来控制每页显示条数。如果没有指定 _limit ,默认每页显示10条。
GET /posts?_page=1
GET /posts?_page=1&_limit=2
排序 Sort
GET /posts?_sort=id&_order=asc #升序
GET /posts?_sort=id&_order=desc #降序
_sort 表示排序字段,_order 表示具体的排序方式,默认是升序:asc降序为:desc。
多字段组合排序
GET /posts?_sort=para1,para2&_order=desc,asc
切片
切片与字符串数组切片类似,可以返回指定范围长度的数据内容,起始下标为0
_start指定纪录起始点,包含起点
_end指定终点,不包含终点
_limit指定返回的数量
GET /posts?_start=0&_end=3
GET /comments?_start=0&_end=2
GET /posts?_start=0&_limit=2
添加数据
使用POST请求可以增加数据,例如我们在Postman中进行如下配置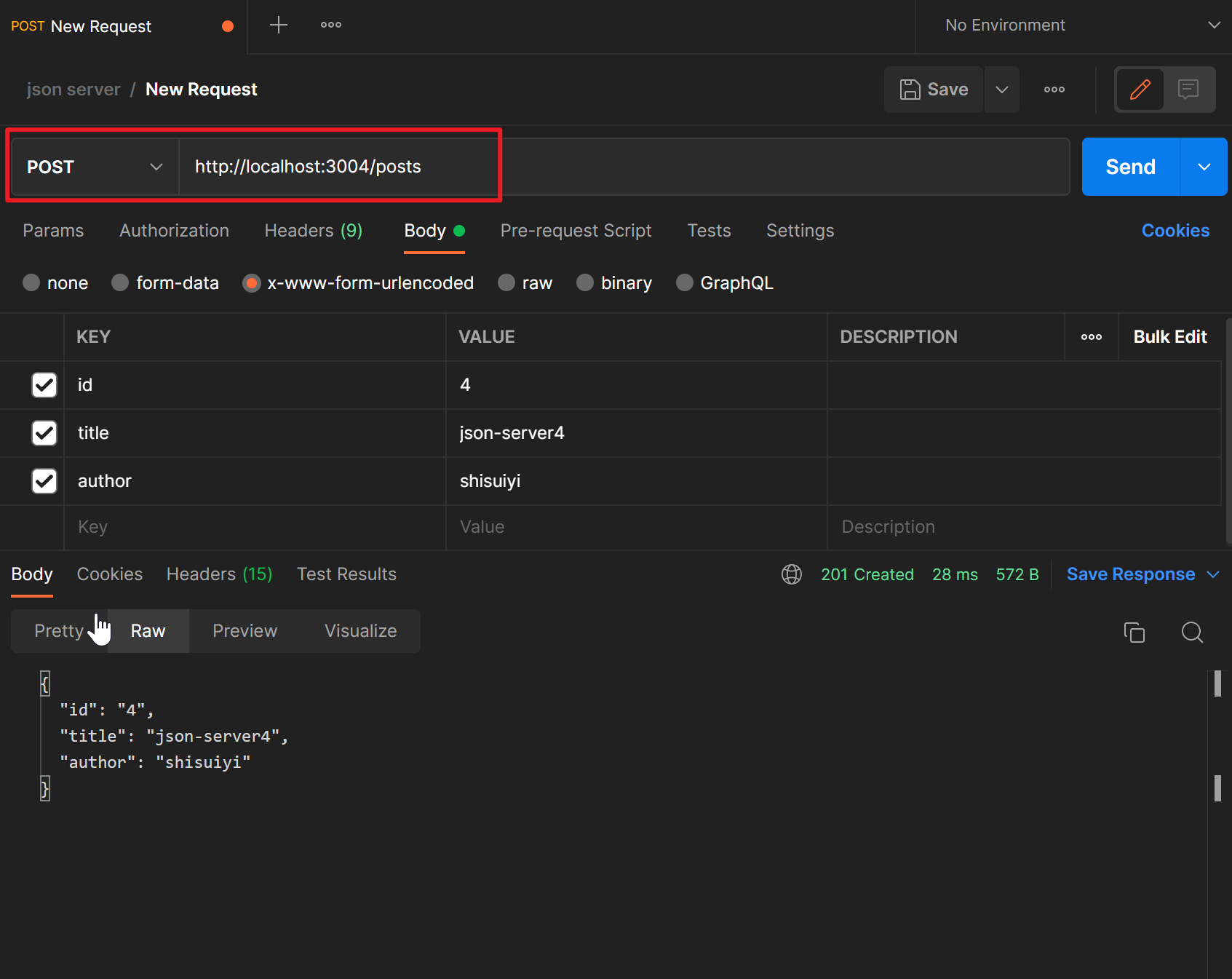
查看一下
[
{
"id": 1,
"title": "json-server",
"author": "typicode"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "json-server2",
"author": "typicode2"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "json-server3",
"author": {
"name": "jack"
}
},
{
"id": "4",
"title": "json-server4",
"author": "shisuiyi"
}
]
或者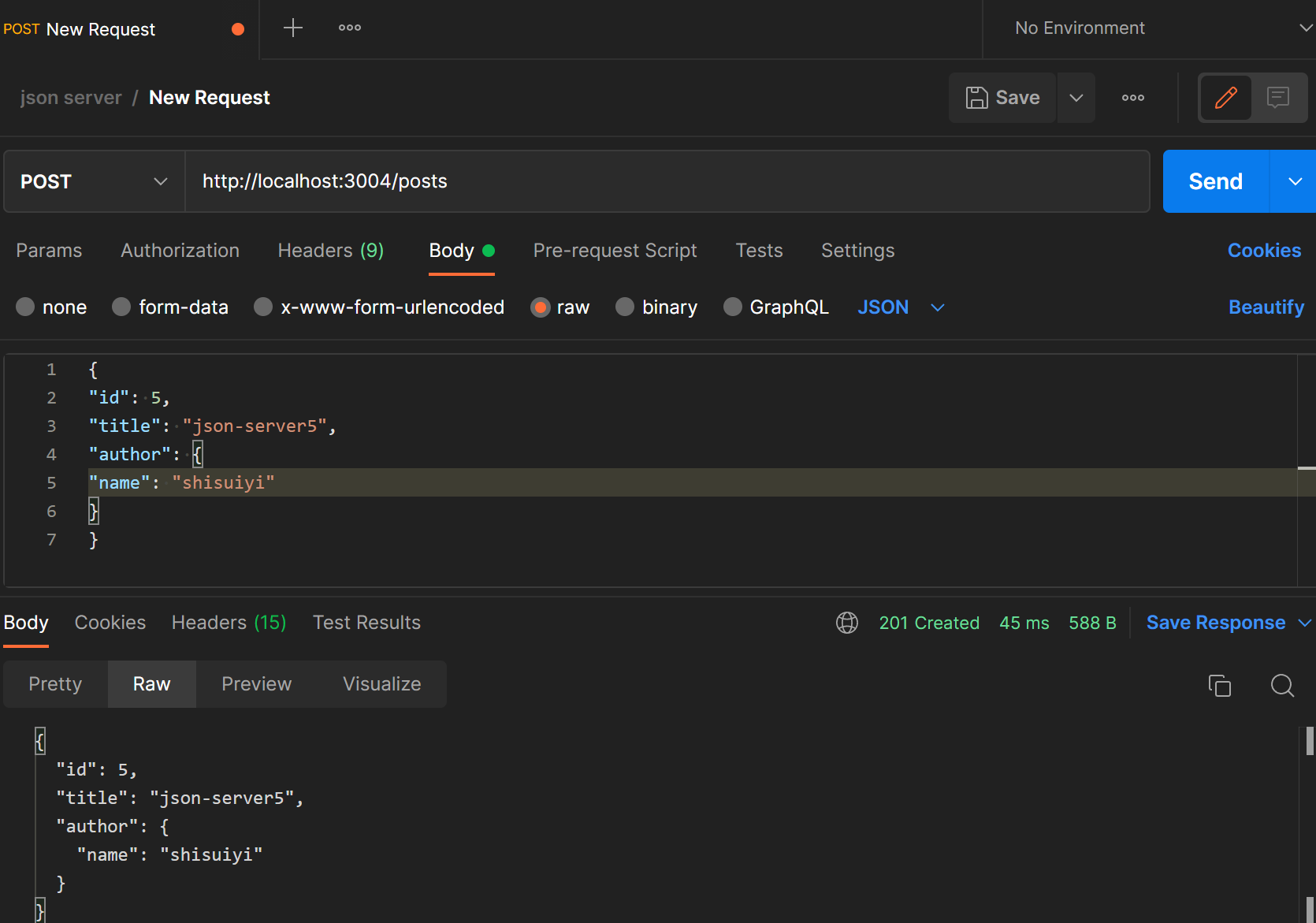
修改数据
使用PATCH或者PUT可以对数据更新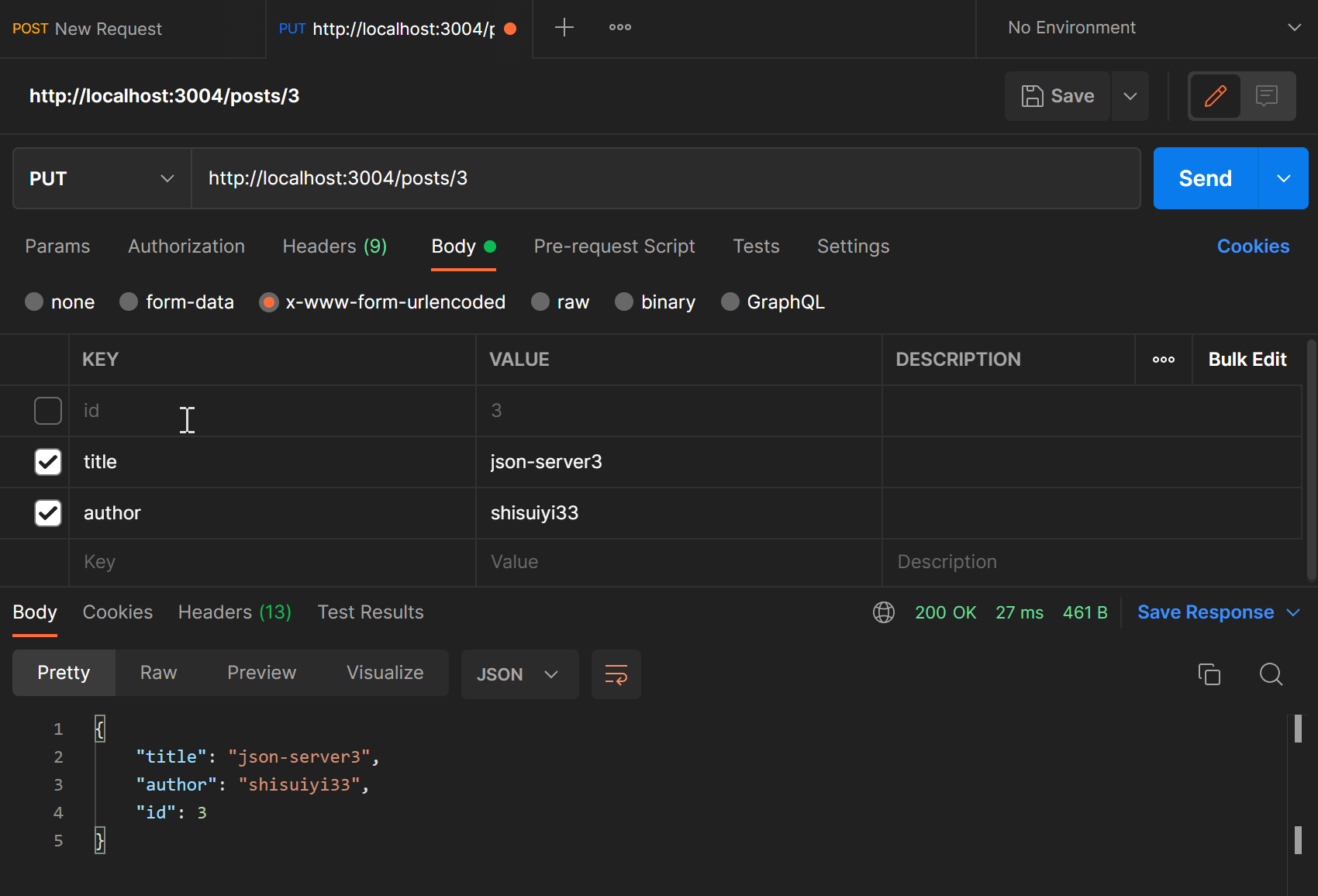
查看一下http://localhost:3004/posts/3
{
"title": "json-server3",
"author": "shisuiyi33",
"id": 3
}
删除
使用DELETE可以删除数据,例如 请求 http://localhost:3004/posts/3 ,则会删除id=3的数据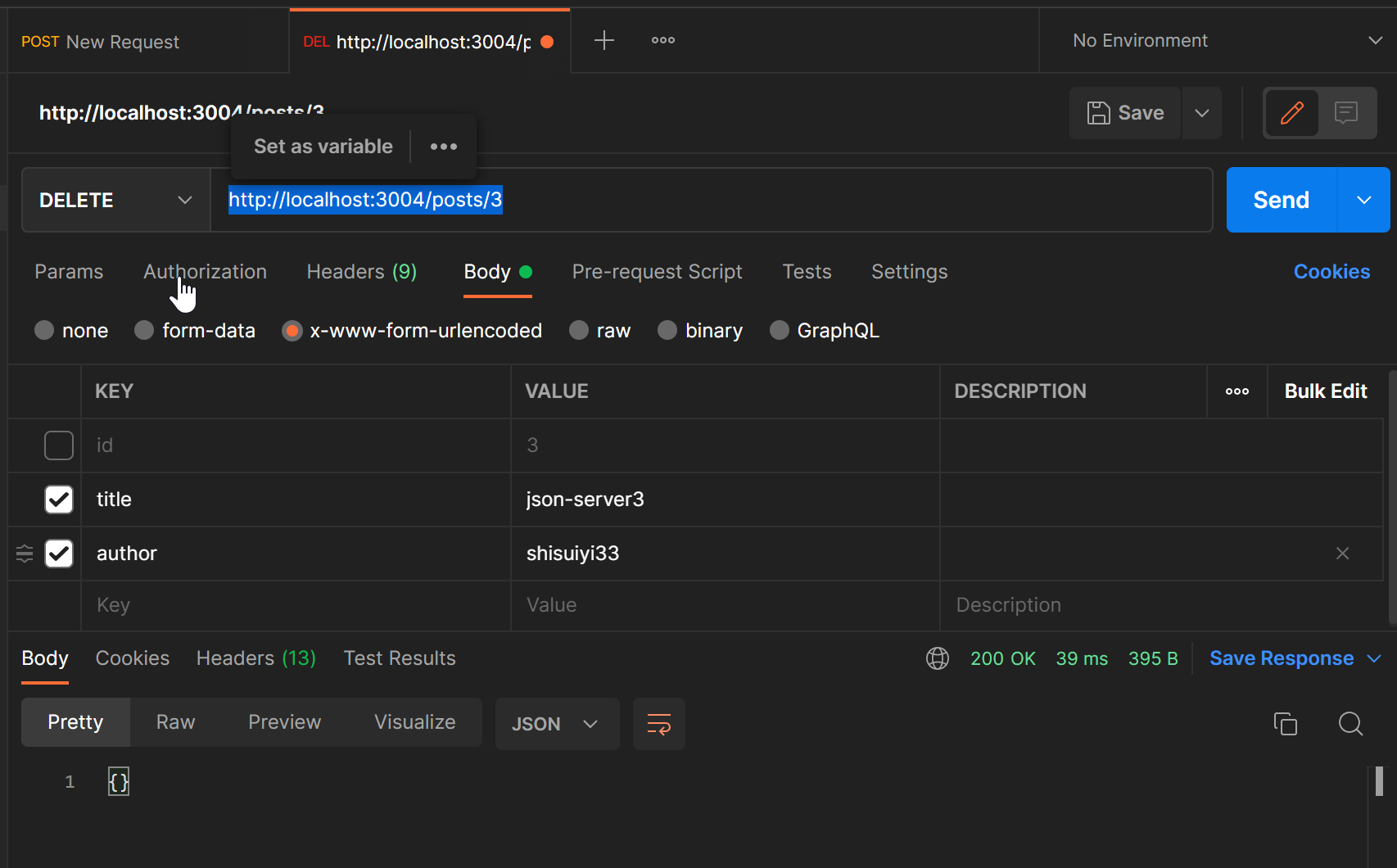
全局搜索
采用 q 来设置搜索内容: http://localhost:3004/posts?q=2
查看db
工具二:Flask
安装第三方模块
通过pip install flask安装(flask是一个轻量级的web开发框架)
验证
在命令行里输入 flask --version 查看Flask是否安装成功
flask模块的使用
简单的示例
模拟一个登录接口
在API文档中说明如果登录成功,返回:状态码:200,
{"status": 200, "msg": "登录成功!", "code": 10000, "token": "xxxx123123123"}
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2022/7/3 14:24
# @Author : shisuiyi
# @File : mock.py
# @Software: win10 Tensorflow1.13.1 python3.9
from flask import Flask, jsonify
# 1. 初始化flask对象
app = Flask(__name__)
# 2. 创建一个函数,并将其装饰为一个mock server
# 定义视图函数,设置路由规则 || 定义接口 模拟返回结果
@app.route("/login", methods=["get", "post"])
def login():
# return {"status": 200, "msg": "登录成功!", "token": "xxxx123123123"}
data = {"status": 200, "msg": "登录成功!", "code": 10000, "token": "xxxx123123123"}
return jsonify(data) #序列化json数据
#jsonfy与json.dumps区别:
# 使用jsonify时响应的Content-Type字段值为application/json,
# 而使用json.dumps时该字段值为text/html。
# 3. 运行
app.run() #使用默认方式启动项目
# app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5566, debug=True) # 以调试模式启动项目
# host='0.0.0.0’,表示可以使用127.0.0.1、1ocahost、ip(192.168.18.3)访问接口
运行后访问 http://127.0.0.1:5000/login
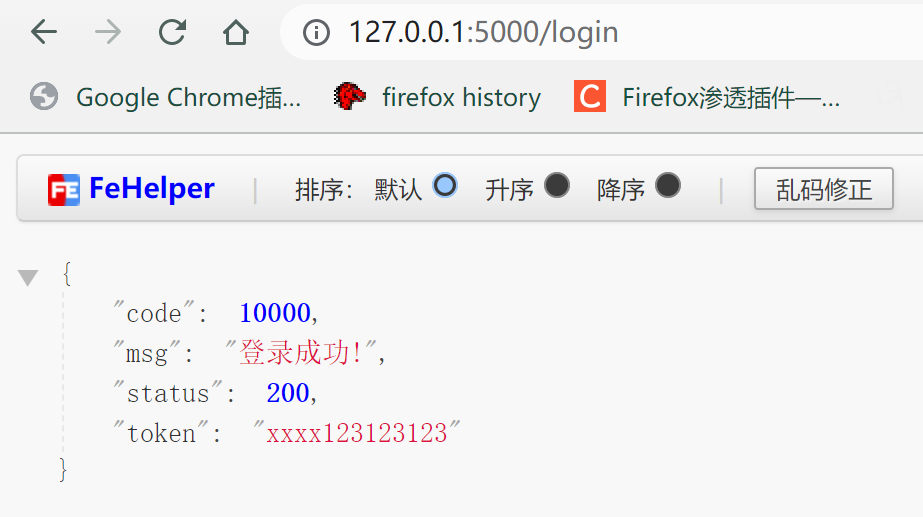
关于flask的详细用法以后再补充
工具三:pook的使用
仓库地址
用于 HTTP 流量模拟和期望的多功能、富有表现力和可破解的实用程序库,在Python中变得容易。深受gock的启发。
基本模拟:示例
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pook
import requests
@pook.on
def test_my_api():
mock = pook.get('http://shibuyu.com/api/1', reply=200, response_json={"status": 200, "msg": "登录成功!", "code": 10000, "token": "xxxx123123123"})
resp = requests.get('http://shibuyu.com/api/1')
print(resp.json())
assert resp.status_code == 200
assert resp.json()['msg'] == "登录成功!"
assert mock.calls == 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_my_api()
# 输出
{'status': 200, 'msg': '登录成功!', 'code': 10000, 'token': 'xxxx123123123'}
Process finished with exit code 0
使用装饰器:示例
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pook
import requests
@pook.get('http://httpbin.org/status/500', reply=204)
@pook.get('http://httpbin.org/status/400', reply=200)
def fetch(url):
return requests.get(url)
res = fetch('http://httpbin.org/status/400')
print('#1 status:', res.status_code)
res = fetch('http://httpbin.org/status/500')
print('#2 status:', res.status_code)
# 输出
#1 status: 200
#2 status: 204
简单unittest集成:示例
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pook
import unittest
import requests
class TestUnitTestEngine(unittest.TestCase):
@pook.on
def test_request(self):
pook.get('server.com/foo').reply(204)
res = requests.get('http://server.com/foo')
self.assertEqual(res.status_code, 204)
def test_request_with_context_manager(self):
with pook.use():
pook.get('server.com/bar', reply=204)
res = requests.get('http://server.com/bar')
self.assertEqual(res.status_code, 205)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
# 输出
205 != 204
Expected :204
Actual :205
<Click to see difference>
test_request_with_context_manager
self.assertEqual(res.status_code, 205)
AssertionError: 204 != 205
Ran 2 tests in 0.015s
FAILED (failures=1)
Process finished with exit code 1
简单pytest集成:示例
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pook
import pytest
import requests
@pook.activate
def test_simple_pook_request():
pook.get('server.com/foo').reply(204)
res = requests.get('http://server.com/foo')
assert res.status_code == 204
@pook.on
def test_enable_engine():
pook.get('server.com/foo').reply(204)
res = requests.get('http://server.com/foo')
assert res.status_code == 204
pook.disable()
@pook.get('server.com/bar', reply=204)
def test_decorator():
res = requests.get('http://server.com/bar')
assert res.status_code == 204
def test_context_manager():
with pook.use():
pook.get('server.com/baz', reply=204)
res = requests.get('http://server.com/baz')
assert res.status_code == 204
@pook.on
def test_no_match_exception():
pook.get('server.com/bar', reply=204)
with pytest.raises(Exception):
requests.get('http://server.com/baz')
# 输出
============================= test session starts =============================
collecting ... collected 5 items
pookdemo.py::test_simple_pook_request PASSED [ 20%]
pookdemo.py::test_enable_engine PASSED [ 40%]
pookdemo.py::test_decorator PASSED [ 60%]
pookdemo.py::test_context_manager PASSED [ 80%]
pookdemo.py::test_no_match_exception PASSED [100%]
============================== 5 passed in 0.49s ==============================
Process finished with exit code 0
将上下文管理器用于隔离的 HTTP 流量拦截块:示例
首先试一下直接访问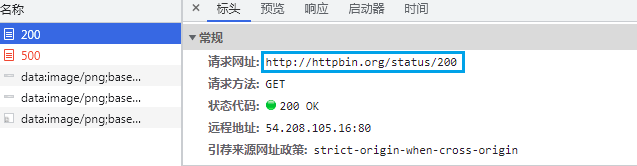
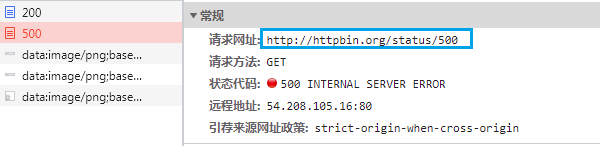
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pook
import unittest
import requests
import pook
import requests
# Enable HTTP traffic interceptor
with pook.use():
pook.get('http://httpbin.org/status/500', reply=204)
res = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/status/500')
print('#1 status:', res.status_code)
# Interception-free HTTP traffic
res = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/status/200')
print('#2 status:', res.status_code)
# 输出
#1 status: 204
#2 status: 200
Process finished with exit code 0
工具四:requests-mock
待续:https://requests-mock.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pytest.html




评论